When it comes to oral health, most people focus on their teeth, often overlooking the importance of healthy gums. However, gums are essential for providing support and protection to your teeth. Unfortunately, gum recession is a prevalent condition that affects many individuals. It occurs when the gum tissue starts to recede, exposing the delicate roots of the teeth. To prevent further damage and maintain a healthy mouth, it is crucial to recognize the signs of gum recession at an early stage. In this blog post, we will delve into the topic of gum recession, explore its causes, and discuss how you can identify the early signs to seek appropriate treatment and preserve your gum health.
What is Gum Recession?
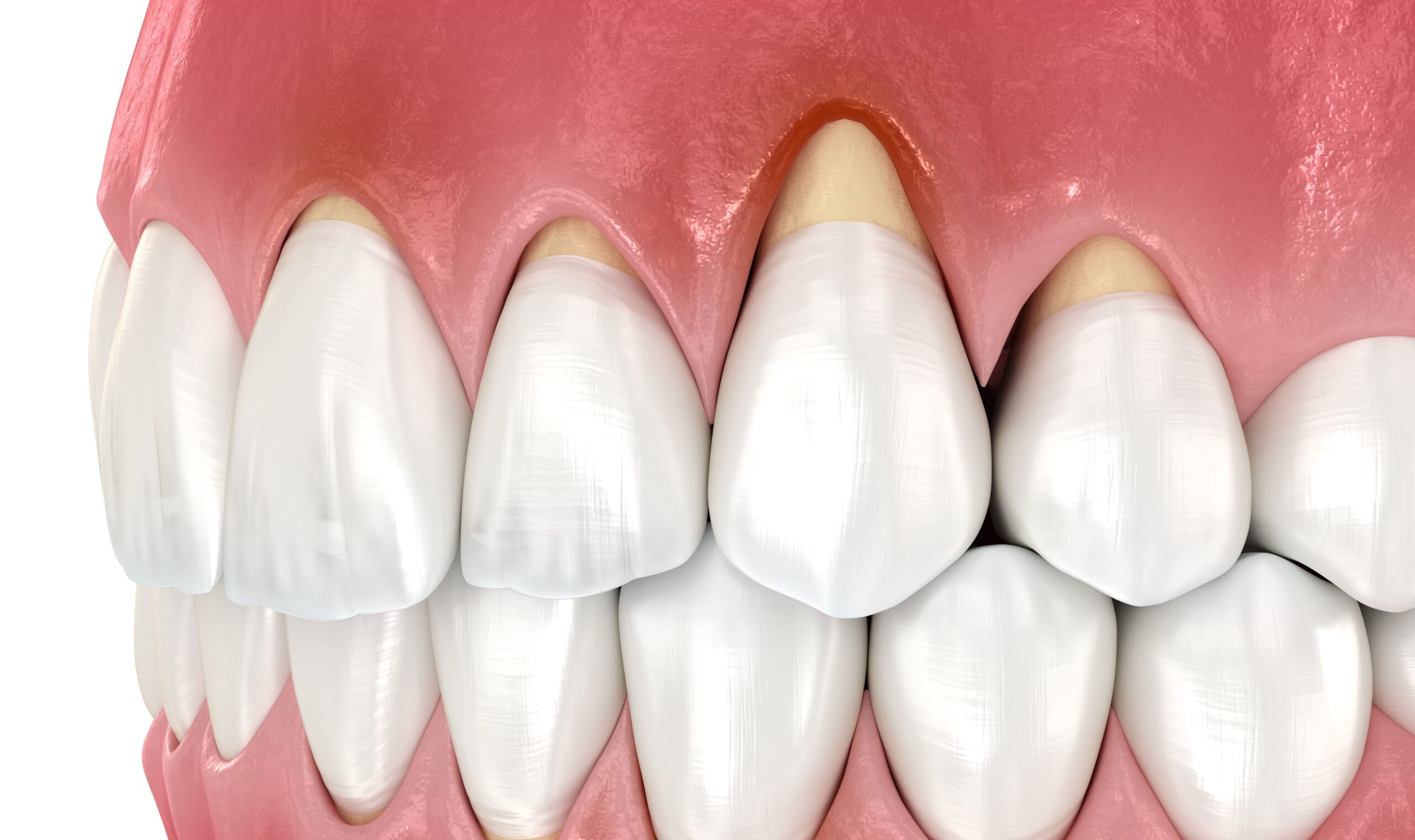
Gum recession is the process of receding of gum tissue from around the teeth. It is also known as gingival recession or, more commonly, receding gums. The condition occurs when the gum line starts to move downward on the tooth surface and exposes part or all of the root. This can lead to many oral health problems such as root sensitivity, increased risk of cavities, and tooth loss. The most common cause of gum recession is inadequate oral hygiene practices. Plaque buildup and tartar accumulation leads to inflammation and infection in the gums, which then causes them to recede. Apart from poor oral hygiene, other factors that can contribute to gum recession include brushing too hard, aggressive flossing, misaligned teeth, certain medical conditions, and aging.
Recognizing the Early Signs of Gum Recession

The earliest signs of gum recession are often subtle and may be difficult to identify. However, if you know what to look for and practice regular oral hygiene habits, you can detect gum recession early and take steps to protect your teeth. The most visible sign is a receding gumline, where the teeth appear longer as more of the tooth surface or root becomes exposed.
Gum recession often leads to increased tooth sensitivity, causing discomfort or pain when consuming hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks. Discoloration of the tooth roots may occur as they become exposed, appearing darker or discolored compared to the rest of the tooth. Notches or indentations at the gumline, known as gumline recession, can be observed. Gum inflammation and bleeding may accompany gum recession, especially during brushing or flossing. Advanced gum recession can result in loose or shifting teeth as the support for the teeth diminishes. Increased gaps or spaces between teeth may also be noticeable. In some cases, gum recession can lead to gum infection or abscess, which may cause pain, swelling, pus discharge, or a bad taste in the mouth. If any of these symptoms are present, it is crucial to seek dental attention promptly. Early detection and treatment of gum recession are vital to prevent further damage and maintain oral health.
It is important to seek professional help for gum recession in various situations. If you notice visible signs of gum recession, such as a receding gumline or exposed tooth roots, it is advisable to schedule an appointment with your dentist. Additionally, persistent or worsening symptoms like tooth sensitivity, pain, gum inflammation, or bleeding should prompt you to seek professional dental care. If your teeth feel loose or if there are changes in your bite or alignment, it is crucial to consult a dental professional for an evaluation. Concerns about gum health or regular dental check-ups are also valid reasons to seek professional help. Regular visits to your dentist allow for comprehensive examinations, accurate diagnoses, and appropriate treatment plans. Seeking timely professional assistance ensures that the extent of gum recession is assessed, underlying causes are identified, and suitable treatments or preventive measures are recommended to preserve gum health and prevent further damage to teeth and supporting structures.
Diagnosing and Treating Gum Recession
Gum recession can be diagnosed by examining the gums for signs of inflammation or receding from the teeth. To do this, use a small mirror and start at the back molars. Look closely for any changes in gum color, texture, or shape. If your gums have thinned and pulled away from your teeth, it could be a sign of gum recession.
It is important to seek professional help for gum recession as soon as possible. If left untreated, the condition can cause serious damage to your teeth and gums, including loss of bone density, tooth decay, and tooth loss. The earlier you receive treatment, the better your chances of preventing long-term damage and preserving your oral health.
Dentists can diagnose gum recession by examining the gums for signs of inflammation or receding from the teeth. During a dental exam, your dentist will use a small mirror to check for any changes in gum color, texture, or shape. They may also measure the depth of your gum pockets or take X-rays to assess the severity of the condition and suggest treatment. Treatment for gum recession can include professional cleaning, scaling and root planing (deep-cleaning of the teeth), antibiotics, or flap surgery. In cases where the bone has been lost due to gum recession, a special procedure may be necessary to help regenerate new bone and tissue. In general, early detection is key to preventing further damage and preserving your oral health.
How to Prevent Gum Recession

Preventing gum recession requires adopting proper oral hygiene practices and making lifestyle choices that promote gum health. To start, maintain a consistent oral hygiene routine by brushing your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Be gentle while brushing, using circular motions along the gumline and all tooth surfaces. Regular flossing is crucial to remove plaque and food particles from between the teeth and gums. Additionally, choose a soft-bristled toothbrush to avoid abrasive damage to the gums. It’s important to practice gentle brushing techniques and avoid aggressive brushing. Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings allow your dentist to monitor gum health, detect early signs of recession, and provide appropriate preventive measures or treatments. Quitting tobacco use is essential as it increases the risk of gum disease and recession. Maintain a balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while minimizing the consumption of sugary and acidic foods. Manage teeth grinding by wearing a mouthguard or splint, and practice stress management techniques to reduce its occurrence. By following these preventive measures and seeking regular dental care, you can significantly reduce the risk of gum recession and maintain optimal gum health.
In Conclusion
Gum recession is a common condition that causes receding of the gums and exposes the root of the tooth. If left untreated, it can lead to other serious complications such as increased sensitivity, infection, tooth loss, and even bone loss. It is important to recognize the early signs of gum recession so that you can seek appropriate treatment and prevent further damage. By practicing good oral hygiene habits, visiting your dentist regularly, and identifying the early signs of gum recession, you can ensure a healthy mouth and protect your teeth for a lifetime.