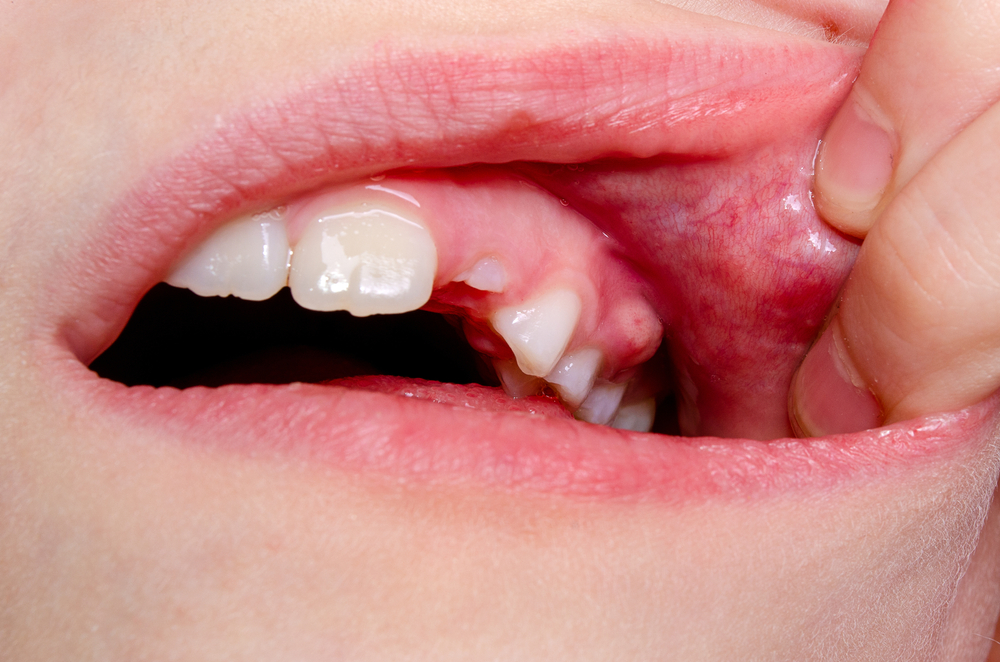
Dealing with a dental abscess can be a distressing experience due to the intense pain and potential for serious complications. This blog aims to provide a comprehensive guide on how to recognize, manage, and treat a dental abscess effectively to regain oral health and prevent future issues.
In This Blog:
- Understanding Dental Abscesses
- Temporary Management of a Dental Abscess
- Professional Treatment Options
Understanding Dental Abscesses
A dental abscess is a localized collection of pus caused by a bacterial infection in the teeth or gums. There are three primary types:
- Periapical Abscess: Occurs at the tooth’s root due to untreated cavities or dental trauma.
- Periodontal Abscess: Develops in the gums next to a tooth root, often associated with advanced gum disease.
- Gingival Abscess: Forms in the gum tissue without affecting the tooth’s root, usually from foreign objects or trapped food particles.
Causes and Risk Factors
Dental abscesses are primarily caused by bacterial infections that develop in the teeth or gums. The most common underlying causes include untreated tooth decay, which allows bacteria to penetrate deep into the tooth pulp, and advanced gum disease, where bacteria accumulate in pockets formed between the gums and teeth. Dental trauma, such as fractures or chips in teeth, can also expose the inner tooth structures to bacteria, leading to infection.
Other risk factors include compromised dental procedures that may expose the tooth to bacteria if not properly sealed, a weakened immune system that reduces the body’s ability to fight infections, and poor oral hygiene habits that promote plaque buildup and increase the likelihood of decay and gum disease. Recognizing these causes and risk factors underscores the importance of regular dental care and maintaining good oral hygiene practices to prevent the development of dental abscesses and other oral health issues.
Recognizing Symptoms
Early detection of a dental abscess is crucial to prevent complications. Key symptoms include:
- Severe, Persistent Toothache: Often throbbing and exacerbated by chewing or pressure.
- Swelling: Around the affected tooth or in the face.
- Sensitivity: To hot or cold temperatures.
- Fever: Indicates a spreading infection.
- Painful, Swollen Lymph Nodes: Under the jaw or in the neck.
It’s important to note that dental abscesses can worsen rapidly if left untreated, potentially leading to more severe symptoms and complications. Therefore, if you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to seek prompt dental care to diagnose and treat the abscess before it progresses further.
Temporary Management of a Dental Abscess
While professional treatment is necessary, you can manage symptoms at home to alleviate discomfort temporarily:
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers like ibuprofen can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- Salt Water Rinse: Gargling with warm salt water several times a day can help cleanse the abscess and reduce swelling.
- Cold Compress: Applying a cold compress to the outside of the cheek near the affected area can numb pain and reduce swelling.
Professional Treatment Options
Seeking professional dental care for a dental abscess is crucial for several reasons. Dentists are trained to accurately diagnose the abscess and determine its severity, which helps in planning the appropriate treatment. Professional dental care involves procedures such as draining the abscess to alleviate pressure and pain, cleaning the affected area to remove bacteria and debris, and prescribing antibiotics if necessary to clear the infection. Additionally, dentists can perform root canal therapy to save the affected tooth or recommend tooth extraction if the tooth cannot be saved.
Prompt treatment not only relieves immediate pain and discomfort but also prevents the infection from spreading to other parts of the mouth or body, reducing the risk of serious complications like sepsis. Moreover, dental professionals can provide guidance on maintaining good oral hygiene practices and preventive care to minimize the likelihood of future dental abscesses. Seeking timely dental care ensures effective treatment and helps preserve overall oral health and well-being.
Drainage
If the abscess is localized and accessible, the dentist may choose to drain it. This involves making a small incision into the abscess to allow the pus to drain out. The area is then cleaned thoroughly with saline solution to remove any remaining pus and bacteria.
Root Canal Therapy
When the abscess originates from an infected tooth pulp (the innermost part of the tooth containing nerves and blood vessels), root canal therapy may be necessary. During this procedure, the dentist removes the infected pulp, cleans and disinfects the root canal, and seals it with a filling material to prevent further infection. A crown may be placed over the treated tooth to restore its strength and appearance.
Antibiotics
In some cases, especially if the infection has spread beyond the immediate area of the abscess or if there is a risk of systemic infection, the dentist may prescribe antibiotics. Antibiotics help to control and eliminate the infection, particularly when combined with other treatments.
Tooth Extraction
If the tooth is severely damaged by decay or if the infection cannot be effectively treated with root canal therapy, extraction may be necessary. Removing the tooth prevents the infection from spreading further and allows for proper healing.
Pain Management
Throughout treatment, dentists prioritize managing pain and discomfort associated with the abscess. This may involve prescribing pain relievers or recommending over-the-counter medications to alleviate symptoms.
Follow-up Care
After initial treatment, follow-up visits may be necessary to monitor healing and ensure the infection has been fully eradicated. Dentists may also provide guidance on oral hygiene practices and lifestyle changes to prevent future abscesses.
Preventing Dental Abscesses
Taking proactive steps to maintain good oral hygiene and regular dental care can significantly reduce the risk of dental abscesses:
- Brushing and Flossing: Daily to remove plaque and bacteria.
- Regular Dental Visits: Every six months for cleanings and check-ups.
- Healthy Diet: Low in sugars and high in fiber-rich foods.
- Avoiding Tobacco: Which increases the risk of gum disease and tooth decay.
Conclusion
Handling a dental abscess involves prompt recognition, home management of symptoms, and seeking professional dental care for effective treatment. By understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, as well as adopting preventive measures, you can protect your oral health and prevent the recurrence of dental abscesses. Remember, early intervention is key to minimizing pain and ensuring a swift recovery to restore your smile and overall well-being.